A budget or laptop PC will come with an integrated graphics card (meaning that it’s plugged in alongside the motherboard). Others have a dedicated card that can be swapped out. You can change out for a different one, and you’ll usually encounter it on premium desktop or gaming computers.
Whether it’s an integrated card or a dedicated card is the same, there will be times when it is necessary to identify the GPU you own. This article will show you how to determine your graphics card’s specs on Windows 11.
What is a graphics card (GPU)?
Though often referred to interchangeably, graphic cards and GPUs are distinct. Also known as video card display adapters or graphic adapters, graphic cards create images and then feed them to the monitor or Display of a computer. To do this, graphics cards comprise various elements, such as the GPU, a graphics processing unit.
The GPU is the brainstem within the card where the required image display processing occurs. After transferring texture data to the memory of your graphics card, the GPU does fast calculations to process the information. When the data is processed, it is returned to RAM before being displayed on the screen, where it will appear as an image or frame in the form of an HD video or game on your computer.
GPU glossary
If you’re looking at the capabilities of your GPU, You’ll likely encounter some jargon. But don’t fret; we’ve got you covered!
This glossary will help you understand GPU terminology to help you determine the performance of the performance of your GPU:
Clock speed: Clock speed refers to the rate at which a GPU’s core is operating to render graphics. It is usually measured in either MHz or GHz. The term “GPU boost clock” refers to the GPU boost clock as the most potent frequency at which the GPU can run at an average speed in terms of its maximum performance.
FPS is a short form for Frames per Second. Or FPS is FPS is the number of images, also known as “frames,” rendered by the GPU and then displayed on your Display per second. FPS is used to gauge how well an app or game is operating. The greater the FPS is, the smoother the rendering.
GDDR graphics Double Data Rate, or GDDR, is a high-speed video memory used to store and retrieve graphics information in the GPU. There are several types and variants of GDDR. Some offer superior video rendering capabilities in comparison to others.
Resolution: Resolution is the number of pixels shown on a display. High resolutions typically need higher GPU capacity to render every frame.
TDP: Thermal Design Power or TDP is the term used to describe the most heat the CPU or GPU can generate in a particular task. It is an essential metric to consider in evaluating GPU cooling strategies.
VRAM: Video Random Access Memory, or VRAM, manages and stores graphic data stored on your GPU. VRAM is essential for displaying large-scale textures, intricate 3D models, and seamless rendering. It’s a memory for your GPU.
How to Check Your Graphics Card With Device Manager
The Windows 11 Device Manager overviews all devices connected to your PC. It helps check the specifications of devices, for example, figuring out the type of graphics card it has. However, it can be used to update your drivers, connect new appliances, and take devices off, as well as other devices.
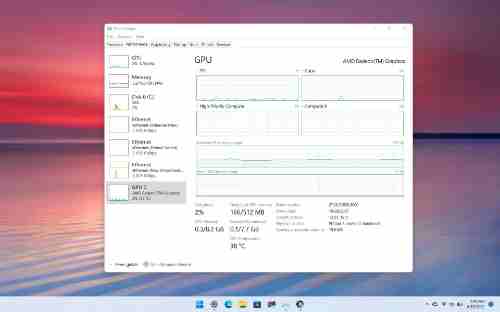
If you own both integrated graphics and a separate graphics card and are using multiple displays, use the DirectX Diagnostic Tool or the Settings application (those steps are listed below) to determine what GPU is linked to what Display.
This is how you can check the GPU with Device Manager:
1. Open the start menu. Search for Device Manager. Press Enter.
2. Double-click Display adapters or click the icon >.
3. Your graphic card will be displayed in this section.
External GPU cards
If you have one, follow these steps to figure out the External GPU (eGPU) you’re using:
The search bar for desktops begins by typing Device Manager and selecting it at the point where it appears.
Select the Display adapters near the top of the entry list. Click the drop-down menu and search for the name, and the model of the eGPU you have installed will remain separate from the built-in GPU in your computer.
External GPUs or a video card is an easy option to enhance the gaming capabilities and graphics experience of –
1111111111.
1a old laptop
that has VGA ports. Be sure to evaluate the quality of your equipment and perform your research before deciding on the right one. In certain instances, you may need to upgrade your laptop completely.
Understanding the graphic card you own is an excellent start. However, knowing how to test the performance of your graphics card in either a notebook or desktop will aid you in understanding the exact specifications and making the best out of it in graphics-intensive work.
Using the Settings app
The option may provide the information you require if your system includes dedicated and integrated GPUs. This is especially true if the system shifts between the two based on the activity level operating -for example, in this scenario, the user may not be able to see the dedicated GPU in any way. If you’re not concerned about the issue, try these instructions:
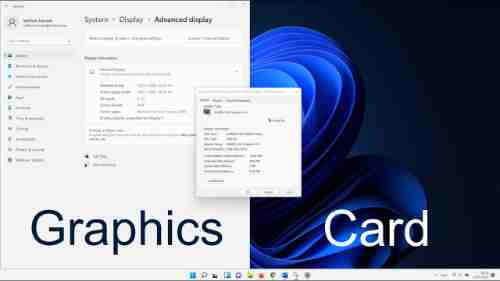
- Within the Settings app, go to the System tab and then Display.
- Click Related settings. Advanced Display.
- GPU details should be found in the Display Information. Additionally, any other GPUs you’re running may not appear here according to your computer’s configuration.
- Using Device Manager
Windows 11 Device Manager
Task Manager is preferred over Device Manager as it gives more significant details. However, unlike the Settings application, there’s no concern about the secondary GPUs being removed from the game.
In the taskbar’s search bar or the Start menu, look up Device Manager and choose the application from the results.
After Device Manager operates, select the arrow icon next to Display adapters. Then, you’ll see all the GPUs installed on the computer.
Check GPU Memory on Windows 11 in 2023
Then, five options exist to verify the GPU names and the memory in Windows 11. We have provided steps for both external and integrated GPUs and the method to determine the graphics card’s memory of Windows 11 PCs. In the end, this is everything we have to say. If you want to check the CPU’s temperature in your Windows 11 computer, follow this guide. If you check the GPU in the Windows PC, head over to our guide to discover the recommended programs. If Desktop Window Manager shows high GPU utilization in Windows 11, you can visit our instructional for a fast solution.